Manual tools are essential for various tasks, offering versatility and precision across industries. From simple hand tools to specialized equipment, they play a crucial role in agriculture, construction, and gardening, ensuring efficiency and safety while addressing specific needs effectively.
Definition and Importance of Manual Tools
Manual tools are non-powered, handheld devices designed to perform specific tasks, relying on human effort for operation. They are indispensable across industries, from agriculture to construction, due to their simplicity, portability, and cost-effectiveness. These tools, such as tijeras de poda, rastrillos, and cuchillos, enable precise control and efficiency in tasks like pruning, digging, and crafting. Their importance lies in their versatility, allowing professionals and DIY enthusiasts to achieve high-quality results without reliance on electricity. Safety measures, such as using guantes de protección, are crucial to prevent accidents. Manual tools also promote sustainability, as they often require less energy and maintenance compared to powered alternatives. Their enduring relevance underscores their value in modern and traditional workflows.
Historical Evolution of Manual Tools
Manual tools have undergone significant evolution, tracing back to ancient times when humans first crafted stone tools for survival. Over millennia, materials progressed from stone to metals like bronze and iron, enhancing durability and functionality. The development of specialized tools, such as tijeras de poda and cuchillos, reflected advancing agricultural and craftsmanship needs. Historical tools like varas and rastrillos were essential for farming, while cuchillos de piedra marked early technological milestones. The transition from manual to powered tools, like sierras mecánicas, highlights technological advancements. Today, companies like Bosch continue to innovate, blending traditional designs with modern materials for professionals and DIY enthusiasts. This evolution underscores the enduring relevance of manual tools, bridging ancient techniques with contemporary demands, ensuring their continued utility across industries. Their historical journey mirrors human ingenuity and adaptability, shaping workflows and industries worldwide.
Types of Manual Tools
Manual tools encompass hand tools, gardening tools like tijeras de poda, agricultural tools such as palas, and construction tools. Bosch offers tools for professionals and bricolajeros.
Hand Tools
Hand tools are essential for precision and versatility in various tasks. They include items like tijeras de poda, cuchillos, and escardadoras, used in agriculture and gardening. Bosch offers high-quality tools for professionals and DIY enthusiasts, ensuring durability and efficiency. These tools are designed for specific tasks, such as pruning or cutting, and are often preferred for their portability and ease of use. Safety measures, like using guantes de protección, are crucial when handling hand tools to prevent accidents. Their simplicity and effectiveness make them indispensable across industries, from agriculture to construction, where manual labor is often required. Hand tools remain a cornerstone of productivity, blending tradition with modern innovation to meet diverse needs.
Gardening Tools
Gardening tools are indispensable for maintaining and nurturing plants. Essential items include tijeras de poda for pruning, rastrillos for soil preparation, and palas for digging. These tools are designed to simplify tasks like planting, weeding, and harvesting. Their versatility allows gardeners to handle various plant care needs efficiently. Safety is crucial, with guantes de protección recommended to prevent injuries. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and sharpening, ensures longevity and effectiveness. Gardening tools are not only practical but also eco-friendly, promoting sustainability in horticulture. Whether for professional landscapers or home gardeners, these tools are vital for achieving healthy plant growth and beautiful outdoor spaces. Their importance lies in their ability to connect humans with nature while fostering productivity and creativity in gardening practices.
Agricultural Tools
Agricultural tools are vital for farming and cultivation, enabling tasks like planting, harvesting, and soil preparation. Common manual tools include tijeras de poda for pruning, varas for support, and rastrillos for soil management. Palas and cuchillos are used for digging and cutting, while escardadoras and injertadores aid in weeding and grafting. These tools are essential for small-scale and organic farming, promoting sustainability. Safety measures, such as using guantes de protección, are crucial to prevent injuries. Regular maintenance ensures tool longevity. Agricultural tools connect tradition with modern practices, supporting food production and eco-friendly farming methods. Their versatility and durability make them indispensable for farmers, ensuring efficient and effective crop management. These tools highlight the importance of manual labor in agriculture, blending simplicity with effectiveness to sustain livelihoods and ecosystems.
Construction Tools
Construction tools are essential for building and repair projects, offering precision and reliability. Manual tools like hammers, screwdrivers, and wrenches are indispensable for tasks such as cutting, drilling, and assembling materials. Safety is paramount, with measures including protector ocular, calzados de seguridad, and guantes de protección mecánica-antivibración to prevent injuries. These tools are designed for durability, ensuring long-term use in demanding environments. Companies like Bosch emphasize quality and innovation in their manual tool ranges, catering to both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. Construction tools play a vital role in shaping infrastructure, combining traditional craftsmanship with modern advancements to deliver robust and efficient solutions. Their versatility and reliability make them a cornerstone of the construction industry, enabling the creation of safe and durable structures. Regular maintenance and proper storage further enhance their performance, ensuring they remain essential for years to come.
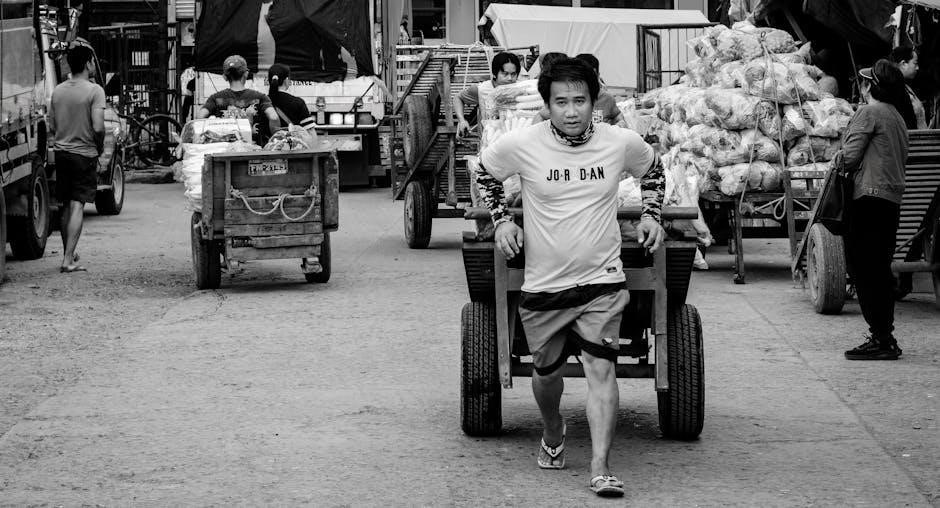

Safety and Maintenance
Proper safety measures and regular maintenance are crucial for manual tools. Use protective gear like safety glasses and gloves. Store tools in dry places and sharpen them when necessary.
Safety Measures When Using Manual Tools
Using manual tools safely is essential to prevent accidents and ensure efficiency. Always wear protective gear like safety glasses, gloves, and secure clothing. Keep long hair tied back and avoid loose jewelry. Ensure tools are in good condition, with sharp edges properly maintained. Store tools in dry, secure locations to prevent damage or misuse. Follow proper handling techniques to avoid strain or injury. Regularly inspect tools for wear and tear, replacing them when necessary. Proper lighting in the workspace is crucial for visibility. Train users on correct tool usage and safety protocols. Adhering to these measures reduces risks, enhances productivity, and prolongs tool lifespan.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper maintenance of manual tools ensures their durability and performance. Regularly clean tools to remove dirt and debris, preventing rust and corrosion. Apply lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and wear. Store tools in a dry, secure location away from direct sunlight. Sharpen cutting tools like knives and pruning shears to maintain effectiveness. Inspect handles for damage and recondition or replace them as needed. Use protective covers or cases to prevent accidental damage. Avoid exposing tools to extreme temperatures or moisture. Schedule routine checks to identify and address wear early. Proper care extends tool lifespan, reduces replacement costs, and ensures reliability in various tasks. Consistent maintenance also enhances safety by preventing tool failure during use.
Applications Across Industries
Manual tools are versatile, serving agriculture, construction, and gardening. They enhance efficiency, precision, and productivity across these industries, making them indispensable for various tasks and projects.

Use in Agriculture
Manual tools are indispensable in agriculture, enabling tasks like pruning, planting, and harvesting. Tools such as pruning shears, hoes, and shovels are essential for crop maintenance and soil preparation. Farmers rely on these tools for precision and efficiency, ensuring high-quality yields. Additionally, manual tools like rakes and pitchforks aid in managing livestock and composting, promoting sustainable farming practices. Their versatility and durability make them vital for small-scale and organic farming, where mechanical alternatives may be less practical. By using manual tools, farmers maintain control over their processes, contributing to food security and environmental stewardship. These tools remain a cornerstone of agricultural productivity, blending tradition with necessity.
Role in Construction
Manual tools are fundamental in construction, enabling precise and efficient tasks. From cutting materials to fitting parts, tools like hammers, screwdrivers, and utility knives are essential. They ensure safety and accuracy in tasks where mechanical tools may not be suitable. For instance, manual tools allow for detailed craftsmanship in finishing work, such as carpentry and plumbing. Their portability and ease of use make them ideal for on-site adjustments and repairs. Additionally, manual tools are cost-effective for small-scale projects and provide a reliable backup when power tools fail. Their versatility ensures that construction professionals can handle a wide range of tasks, from demolition to final touches, making them indispensable in the industry.
Importance in Gardening
Manual tools are indispensable in gardening, enabling precise and efficient tasks. Tools like pruning shears, rakes, shovels, and weeders are essential for plant care and soil management. They allow gardeners to perform tasks such as pruning, planting, and weeding with accuracy and control. Manual tools are cost-effective and eco-friendly, as they eliminate the need for fuel-powered equipment; Their portability and ease of use make them ideal for small-scale gardening projects. Additionally, manual tools promote a connection with nature, fostering a sense of accomplishment and sustainability. They are versatile, catering to various gardening needs, from cultivating soil to harvesting crops. Overall, manual tools are vital for maintaining healthy plants and ensuring a productive garden, making them a cornerstone of gardening practices worldwide.
Environmental Impact
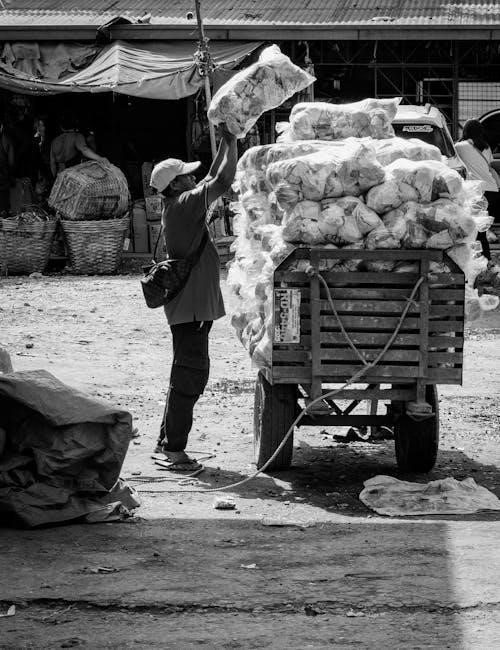

Manual tools promote sustainability by reducing reliance on powered equipment, lowering emissions, and minimizing waste. Eco-friendly materials and durable designs contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.

Eco-Friendly Manual Tools
The shift toward eco-friendly manual tools reflects a growing commitment to sustainability. Many manufacturers now use recycled materials, such as recycled metals and sustainably sourced wood, to produce these tools. This approach reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste and conserving natural resources. Additionally, eco-friendly tools often require less energy for production, lowering carbon emissions. Biodegradable handles and non-toxic coatings further enhance their environmental benefits. Companies like Bosch are investing in eco-conscious designs, catering to both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. These tools not only align with global sustainability goals but also encourage users to adopt greener practices. By choosing eco-friendly manual tools, individuals and industries can contribute to a healthier planet while maintaining productivity and efficiency.
Sustainability in Tool Production
Sustainability in tool production is a growing priority, with manufacturers adopting eco-conscious practices to reduce environmental impact. Many companies now utilize recycled materials, such as recycled steel and aluminum, to craft durable tools while minimizing waste. Energy-efficient manufacturing processes and renewable energy sources are increasingly being implemented to lower carbon footprints. Additionally, biodegradable and non-toxic components are being integrated into tool designs. Certifications like ISO 14001 encourage companies to adhere to strict environmental standards. Brands like Bosch are leading the way by incorporating sustainable practices into their production lines, ensuring tools are both high-quality and eco-friendly. This shift not only benefits the environment but also aligns with consumer demand for greener products, fostering a more sustainable future for the industry.
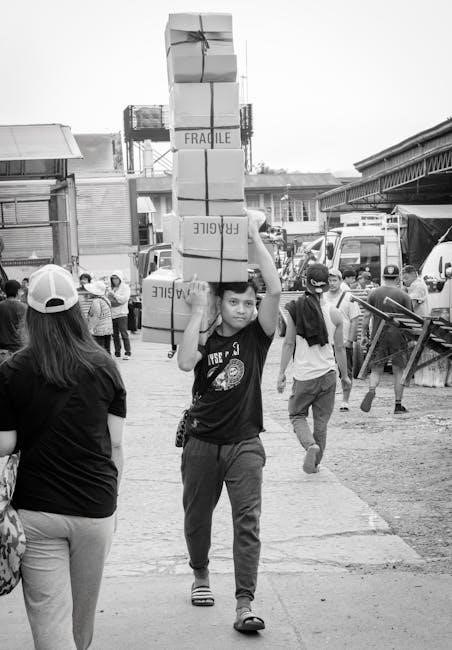

Future Trends and Innovations

Manual tools are evolving with technological advancements, featuring advanced materials and ergonomic designs. Smart tools with sensor technology are emerging, enhancing efficiency and precision. Sustainable practices are also shaping their development, ensuring durability while reducing environmental impact.

Modern Materials and Designs
Modern manual tools are being revolutionized by innovative materials and designs. Lightweight yet durable options like titanium and carbon fiber are becoming popular, reducing fatigue while maintaining strength. Ergonomic handles and adjustable grips enhance comfort and precision, catering to diverse user needs. Additionally, manufacturers are incorporating smart technology, such as sensors and Bluetooth connectivity, to monitor tool performance and improve efficiency. Sustainable materials, like recycled metals and biodegradable plastics, are also gaining traction, aligning with eco-friendly trends. These advancements not only improve functionality but also extend tool longevity, making manual tools more adaptable to evolving industrial demands while prioritizing user safety and environmental responsibility.

Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are transforming manual tools, enhancing their efficiency and functionality. Smart tools now feature integrated sensors and Bluetooth connectivity, allowing users to monitor performance and receive real-time feedback. AI-driven systems optimize tool usage, reducing wear and tear. Additionally, IoT-enabled tools enable remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, ensuring optimal performance. These innovations are complemented by ergonomic designs that prioritize user comfort and safety. For instance, vibration-reducing handles and adjustable grips minimize fatigue during extended use. Furthermore, advancements in motor technology have led to quieter and more energy-efficient tools, making them suitable for diverse environments. These technological integrations not only improve productivity but also cater to the evolving needs of professionals and DIY enthusiasts, ensuring tools remain relevant in a rapidly changing world.
Choosing the Right Tool
Selecting the right manual tool involves understanding the task, considering tool quality, and ensuring proper fit and ergonomics to maximize efficiency and safety while minimizing fatigue.
Factors to Consider
When selecting manual tools, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and safety. First, assess the specific task requirements to choose the right tool for the job. Material quality and durability are crucial, as they directly impact tool longevity. Ergonomics and comfort should not be overlooked, as they reduce fatigue and improve efficiency. Additionally, consider the tool’s weight, balance, and handle design for better control. Compatibility with other equipment or accessories is another key factor. Budget and brand reputation also play a role, as investing in reputable brands often ensures higher quality. Finally, evaluate the tool’s maintenance needs and storage requirements to ensure long-term usability. By carefully considering these factors, users can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and safety.
Best Practices for Selection
Selecting the right manual tools requires a strategic approach to ensure efficiency and safety. Always align the tool with the specific task to avoid damage or inefficiency. Assess the tool’s quality and durability, prioritizing materials that withstand heavy use. Ergonomics should be a priority to reduce fatigue and improve control. Consider safety features, such as slip-resistant handles or protective guards, to minimize accidents. Additionally, evaluate the tool’s compatibility with other equipment or accessories. Budget is a key factor, but investing in reputable brands often ensures better performance and longevity. Finally, consider the tool’s maintenance requirements and storage needs to ensure prolonged usability. By following these best practices, users can optimize their workflow and achieve superior results in various applications.